Written by Josh A.
1. Introduction
The UK fast-food industry is characterised by the severe competition between local and international chains that are currently trying to maintain their profitability in the declining post-Brexit economy (Lubin, 2016). The analysed Subway company is one of the most successful organisations in this segment on the global scale (Harwell, 2015). However, this chain is currently experiencing multiple problems caused by its expansive growth and the growing pressure from the competitors in the UK market (Peterson, 2016). The aim of this report is to identify specific gaps in the current marketing strategy of Subway and formulate practical recommendations on addressing the identified inefficiencies.
2. Situation Analysis
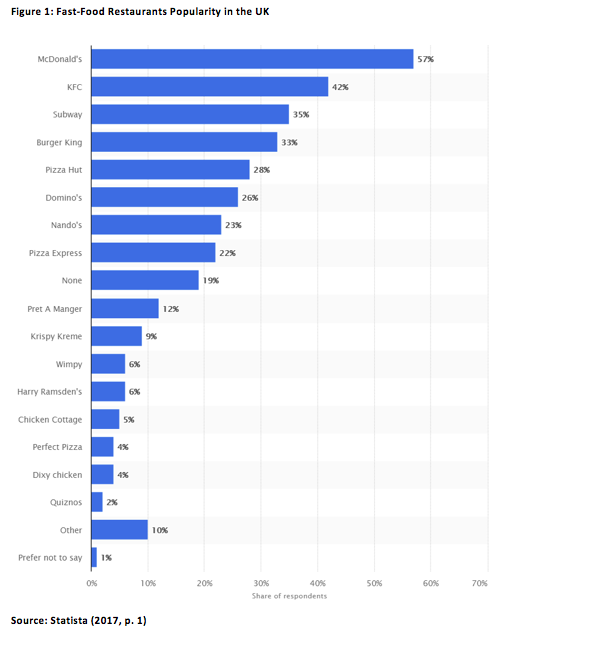
The analysed company is currently the third most popular fast-food chain in the UK according to the 2015 survey data (Statista, 2017). This competitive pressure is further increased by multiple negative environmental factors existing in the UK market such as pound depreciation and post-Brexit uncertainty (BBC, 2017a). This section includes three primary macro-environment and micro-environment analyses that identify existing strategic inefficiencies and substantiate further recommendations to the company.
2.1. PESTLE
The PESTLE macro-environment analysis is highly useful for identifying the external trends that influence specific geographical regions within the scope of their political, economic, social, technological, legal and environmental dimensions (West et al., 2015).
Political
The situation in the UK is currently destabilised by Brexit or the exit from the all-European political partnership (Hunt and Wheeler, 2017). The consequences of this decision are still being realised and may result in substantial changes in the spheres of taxation, import regulations and employment policies.
Economic
The earlier mentioned political decisions resulted in the decreasing purchasing capacity of UK customers due to pound depreciation (Elliott, 2017), which may negatively affect the spending on fast-food products and eating out.
Social
Multiple UK restaurants are already experiencing the consequences of Brexit associated with the departure of EU workers from the country due to the new visa regulations (Rumney, 2017). This situation is highly concerning because experts predict severe workforce availability problems in this segment in the future.
Technological
Subway is attempting to overcome a recent decline in sales by introducing such technological capabilities as self-ordering kiosks and mobile functionality allowing customers to make pre-orders and pick them at specific locations (Patton, 2017).
Legal
In 2019, the UK will have a completely separate jurisdiction from the EU (Hunt and Wheeler, 2017). This may substantiate the need to update corporate policies in order to comply with these regulations.
Environmental
Subway has substantially reduced the emissions by optimising its distribution operations and is actively utilising recycling programmes and sustainable packaging principles in its daily operations (Subway, 2017a), which is highly positive for compliance with the tightening regulations in this sphere in the UK (Nielsen, 2017).
2.2. SWOT
The SWOT framework is applied by marketers to identify specific strengths and weaknesses or organisations and analyse which opportunities and threats can influence their business operations (Fleisher and Bensoussan, 2015).
Strengths
- Subway is an established brand that has good geographical coverage in the UK and is one of the largest fast-food chains in the country (BBC, 2017b).
- Individual restaurants are operating as franchisees and are forced to purchase all ingredients from the central supplier, which guarantees good quality (Subway, 2017b).
Weaknesses
- Franchise-based systems are frequently suffering from customer service fluctuations across different restaurants, which negatively affect the brand image (Leonidou et al., 2017).
- The sales in the UK are currently declining and the market is fairly saturated and may not accept a large number of new Subway franchisees (Peterson, 2016).
Opportunities
- Self-ordering outlets (Patton, 2017).
- Mobile pre-order functionality (Patton, 2017).
Threats
- Increasing competition from local fast food chains such as McDonald’s (BBC, 2017a).
- Decreasing purchase capacity of UK customers due to the pound depreciation (Rees, 2017).
2.3. Porter’s Five Forces
Porter’s Five Forces analysis is utilised to explore the external competitive environment within the scope of the bargaining power of buyers, the bargaining power of suppliers, the threat of new entrants, the threat of substitutes and the degree of competitive rivalry (Rao and Klein, 2013).
The Bargaining Power of Customers – High
Multiple international and local fast-food chains operate in the UK market and customers can choose between them without any switching costs (Lubin, 2016; Statista, 2017).
The Bargaining Power of Suppliers – Medium
The company is working with multiple vendors and does not rely on any organisation exclusively (Subway, 2017b). However, a change of suppliers may result in short-term supply disruptions and should ideally be avoided.
The Threat of New Entrants – Medium
The entry into the UK fast food market requires substantial resources on part of other major chains because these companies need to invest into the development of infrastructure and supply chain organisation to support their franchisees (Wahlen et al., 2017)
The Threat of Substitutes – Medium
Fast food products are non-unique and major chains offer approximately the same set of food products and beverages (Singh and Pattanayak, 2016). However, the customer experience may vary as each company has different servicing standards and restaurant interior standards.
The Degree of Competitive Rivalry – High
Subway is competing with a large number of competitors in the UK fast food industry (Lubin, 2016). On the one hand, it offers sandwiches that are compatible with the food habits of UK consumers and differ from burgers offered by its rivals. On the other hand, the chain has less coverage in comparison with its two primary competitors, McDonald’s and KFC (Statista, 2017).
3. SMART Objectives
The principle of SMART goal setting assumes that organisational objectives must be specific, measurable, agreed, realistic and time-related (Surridge and Gillespie, 2017). The current problems of Subway identified in the previous section suggest that the company should achieve the following objectives.
- To increase Subway’s share in the UK market by 5% within the next year of operation.
- To increase Subway’s profitability by 15% in the next year of operation.
4. Marketing Strategy
The concept of the marketing mix is used to analyse the four primary dimensions of marketing management and sales, namely product, price, promotion and place (Anusha, 2016).
Product
The current criticisms in this dimension are associated with the lack of salads and special options such as breakfast menus that are offered by key competitors including McDonald’s (Peterson, 2016). At the same time, the customers are concerned with the presence of artificial additives in Subway sandwiches and the use of antibiotic-treated meat. Hence, the optimal way to address these criticisms is to start offering salads and breakfast menu options and to adjust sourcing practices so that the demands of health-oriented customers are satisfied.
Price
The company made attempts to introduce additional charges for toasting sandwiches in 2017 (Turrill, 2017), which was negatively received by Subway customers. While a price increase may be necessary considering the growing taxation burden, the state of the UK economy and pound depreciation may negatively influence the purchase capacity of consumers (Rees, 2017) and the company may lose a large share of its clients. This problem can potentially be addressed through offering discounts for mobile pre-orders, scheduled pick-up orders and meal-of-the day orders (Peterson, 2016). While this will not completely mitigate the dissatisfaction caused by the overall price increase, it can demonstrate consumers that the company is looking for ways to reduce the inconvenience for them.
Promotion
The changes in the previous dimensions should be reflected in appropriate social media publications, online and offline advertising to inform consumers about the steps taken by the company to satisfy their demands (Surridge and Gillespie, 2017).
Place
The problem of market oversaturation mentioned by Peterson (2016) must be thoroughly analysed by the company in order to optimise its franchisee location and avoid the theft of consumers from old franchisees by new applicants. It is also possible to offer some underperforming outlets to move their businesses to more attractive spots within their region, which will also improve the accessibility of Subway restaurants for customers.
5. Implementation Plan
The following implementation plan enlists specific strategic activities that can assist Subway in achieving the SMART objectives formulated earlier.
6. Summary
It can be summarised that Subway’s operations in the UK market are negatively influenced by the increasing market saturation and decreasing purchasing capacity of its customers (Peterson, 2016; Turrill, 2017). The ability to implement strategic changes in the price dimension is limited due to the recent economic decline in the UK. However, it is possible to introduce new products demanded by customers, optimise restaurant location schemes and offer new purchase options utilising modern technologies and simplifying customer servicing for both the company and the clients. At the same time, Subway should start preparing for the post-Brexit consequences such as the labour pool reduction and potential changes in the regulatory environment (Hunt and Wheeler, 2017). The focus on franchisee operations optimisation and the revision of supply chain arrangements to accommodate new products and healthier sourcing practices may assist the company in improving its competitive position in the UK fast-food industry.
References
Anusha, K. (2016) “Brand and Marketing Mix-A Review”, Journal of Global Economics, 4 (219), pp. 1-4.
BBC (2017a) “Sandwich chain Subway plans expansion in High Street war”, [online] Available at: http://www.bbc.com/news/business-40488135 [Accessed on 17 November 2017].
BBC (2017b) “Subway: What's behind the sandwich chain's UK success?”, [online] Available at: http://www.bbc.com/news/business-40497482 [Accessed on 17 November 2017].
Elliott, L. (2017) “Brexit economy: sterling fall hits public finances and fails to boost trade”, [online] Available at: https://www.theguardian.com/politics/2017/jul/24/brexit-economy-sterling-fall-hits-public-finances-and-fails-to-boost-trade [Accessed on 17 November 2017].
Fleisher, C. and Bensoussan, B. (2015) Business and competitive analysis: effective application of new and classic methods, New York: FT Press.
Harwell, D. (2015) “The rise and fall of Subway, the world’s biggest food chain”, [online] Available at: https://www.washingtonpost.com/business/economy/the-rise-and-fall-of-subway-the-worlds-biggest-food-chain/2015/05/29/0ca0a84a-fa7a-11e4-a13c-193b1241d51a_story.html?utm_term=.5db0edab8046 [Accessed on 17 November 2017].
Hunt, A. and Wheeler, B. (2017) “Brexit: All you need to know about the UK leaving the EU”, [online] http://www.bbc.com/news/uk-politics-32810887 Accessed on 17 November 2017].
Leonidou, L., Katsikeas, C., Samiee, S. and Aykol, B. (2017) Advances in Global Marketing: A Research Anthology, Berlin: Springer Science & Business Media.
Lubin, R. (2016) “UK's top fast food chain revealed - is your favourite one of them?”, [online] Available at: http://www.mirror.co.uk/news/uk-news/uks-top-fast-food-chain-7613995 [Accessed on 17 November 2017].
Nielsen, A. (2017) “European commission issues 'final warning' to UK over air pollution breaches”, [online] Available at: https://www.theguardian.com/environment/2017/feb/15/european-commission-issues-final-warning-to-uk-over-air-pollution-breaches [Accessed on 17 November 2017].
Patton, L. (2017) “Subway Looks to Fix Its Sales Slump With Tech Upgrades”, [online] Available at: https://www.bloomberg.com/news/articles/2017-06-15/subway-looks-to-fix-its-low-tech-image-after-u-s-sales-slump [Accessed on 17 November 2017].
Peterson, H. (2016) “Subway is facing 2 problems that are wrecking its business”, [online] Available at: http://uk.businessinsider.com/subway-sales-are-declining-2016-5?r=US&IR=T [Accessed on 17 November 2017].
Rao, P. and Klein, J. (2013) Strategies for high-tech firms: marketing, economic, and legal issues, London: ME Sharpe.
Rees, T. (2017) “Pound falls after surprise drop in UK inflation to 2.6pc”, [online] Available at: http://www.telegraph.co.uk/business/2017/07/18/pound-advances-dollar-ahead-key-uk-inflation-data/ [Accessed on 17 November 2017].
Rumney, E. (2017) “Brexit: Restaurants and hotels feel the pinch as EU workers leave the UK”, [online] Available at: http://www.independent.co.uk/news/business/analysis-and-features/brexit-latest-news-restaurants-eu-workers-hotels-leave-uk-europeans-a7946246.html [Accessed on 17 November 2017].
Singh, P. and Pattanayak, J. (2016) “Study of the Relationship among the Factors of Brand Equity: A Study on Fast-food Brands”, Global Business Review, 17 (5), pp. 1227-1239.
Statista (2017) “Which fast food (quick service) restaurants do you go to, if any?”, [online] Available at: https://www.statista.com/statistics/527217/leading-fast-food-restaurants-in-the-united-kingdom-uk/ [Accessed on 17 November 2017].
Subway (2017a) “Environmental Leadership”, [online] Available at: http://www.subway.com/en-gb/aboutus/socialresponsibility/environmentalleadership [Accessed on 17 November 2017].
Subway (2017b) “Support network”, [online] Available at: https://subwayfranchising.com/en-gb/franchise/support-network [Accessed on 17 November 2017].
Surridge, M. and Gillespie, A. (2017) WJEC and Eduqas GCSE Business, London: Hatchett UK.
Turrill, K. (2017) “Subway UK could soon charge you extra if you want your sandwich toasted - and THIS is why”, [online] Available at: https://www.express.co.uk/life-style/food/840103/subway-uk-start-charging-customers-hot-food [Accessed on 17 November 2017].
Wahlen, J., Baginski, S. and Bradshaw, M. (2017) Financial reporting, financial statement analysis and valuation, Boston: Cengage Learning.
West, D., Ford, J. and Ibrahim, E. (2015) Strategic Marketing: Creating Competitive Advantage, London: Oxford University Press.
Yeomans, D. and Rogers, P. (2017) Project Management Made Simple and Effective, Indianopolis: Dog Ear Publishing.